1. Introduction
What is Weight Loss and Why Does It Matter?
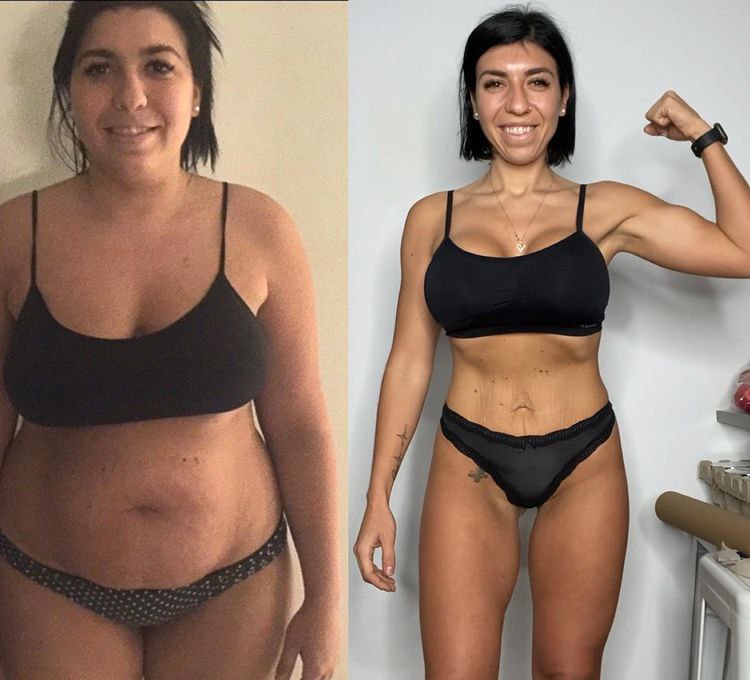
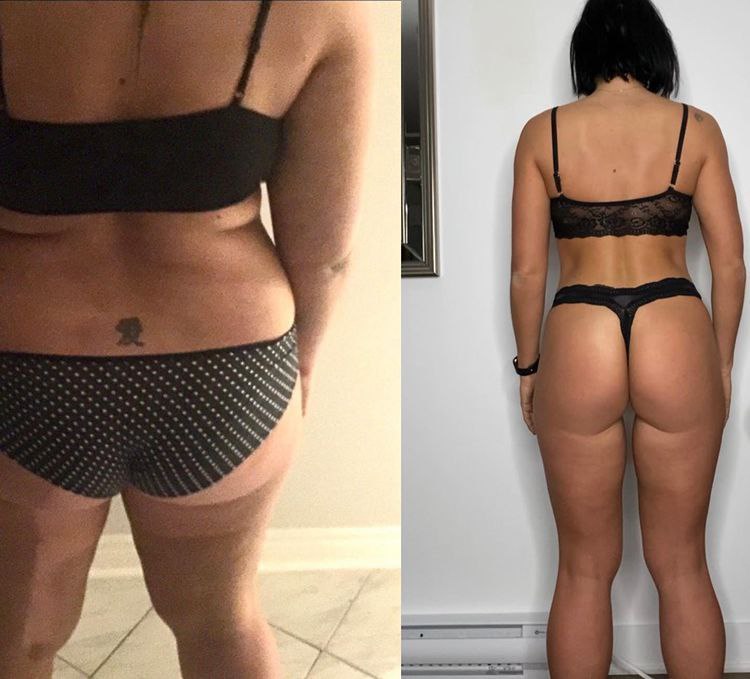
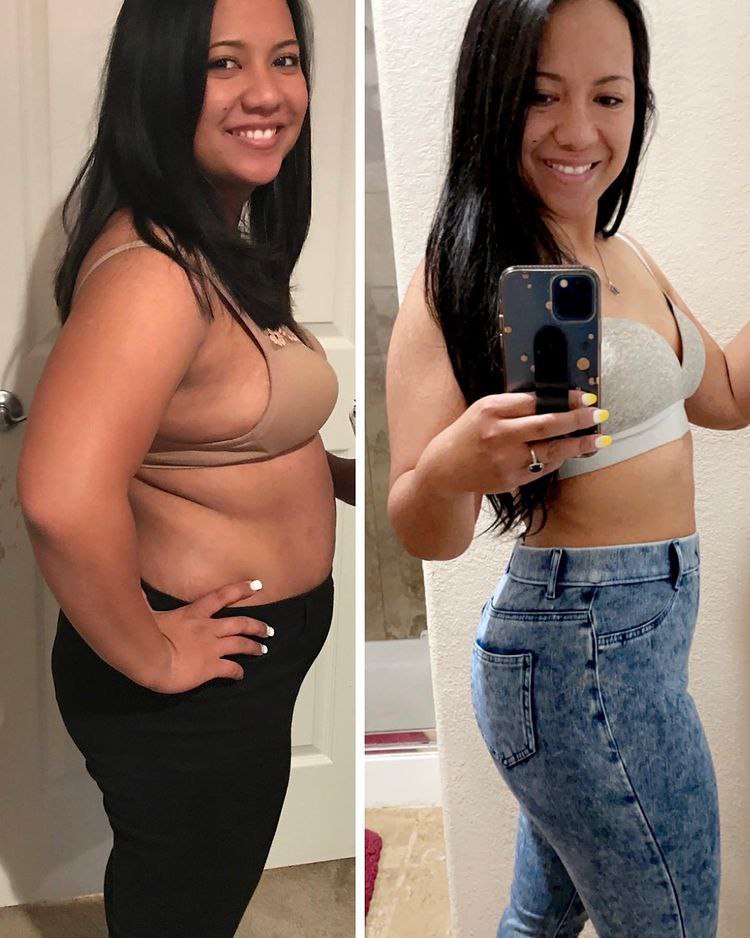
Weight loss is a reduction in body weight, primarily due to the loss of fat. Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight is essential for overall well-being, as it can reduce the risk of chronic diseases like diabetes, heart disease, and certain cancers. Beyond physical health, weight loss can also improve mental health, self-esteem, and overall quality of life.
Overview of This Article
This article will explore the science behind weight loss, common myths, popular weight loss methods, and the importance of maintaining a balanced diet. We’ll also touch on the mental and emotional aspects of weight loss, and how tracking progress can lead to long-term success. Insights from experts and case studies will provide a well-rounded understanding of sustainable weight loss.
2. Understanding Weight Loss
The Science Behind Weight Loss
At its core, weight loss revolves around creating a calorie deficit, meaning you consume fewer calories than your body uses for energy. When the body doesn’t receive enough calories from food, it taps into stored fat to make up the difference, leading to fat loss.
Calories In vs. Calories Out
Weight loss is largely a numbers game. The calories you consume (calories in) must be fewer than the calories you burn (calories out) through daily activities and exercise. However, the type of calories you consume also plays a crucial role in how your body processes food and loses weight.
Role of Metabolism
Metabolism refers to the chemical processes that occur within the body to maintain life, including converting food into energy. People with faster metabolisms burn calories more quickly, while those with slower metabolisms may find it harder to lose weight. Age, genetics, and muscle mass all influence metabolism.
3. Common Weight Loss Myths
Myth 1: All Calories Are Equal
While it’s true that a calorie is a unit of energy, not all calories are equal in how they affect the body. Calories from nutrient-dense foods like fruits and vegetables fuel the body more efficiently than calories from processed junk foods.
Myth 2: You Can Lose Weight Fast and Keep It Off
Rapid weight loss often leads to muscle loss, nutritional deficiencies, and a slowdown in metabolism, making it more difficult to maintain weight loss long-term. Sustainable weight loss occurs at a slower pace, about 1-2 pounds per week.
Myth 3: Exercise Alone is Enough
While exercise is important for weight loss, it must be paired with a healthy diet. Exercise alone cannot offset poor eating habits, and focusing on diet is essential for creating the necessary calorie deficit.
4. Popular Weight Loss Methods
Diet Plans (Keto, Paleo, Intermittent Fasting)
Several diet plans have gained popularity in recent years. The ketogenic (keto) diet focuses on high-fat, low-carb intake, forcing the body into a fat-burning state called ketosis. Paleo emphasizes whole foods, avoiding processed items. Intermittent fasting alternates between periods of eating and fasting to control calorie intake.
Exercise Regimens (Cardio, Strength Training, HIIT)
Exercise is vital for weight loss and overall health. Cardiovascular exercises like running and cycling burn calories, while strength training builds muscle mass, which increases metabolism. High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) combines both cardio and strength in short bursts, maximizing fat burn in less time.
Role of Supplements
Weight loss supplements, including fat burners, protein powders, and appetite suppressants, are often marketed as quick fixes. While some may aid in weight loss, they’re no substitute for a healthy diet and regular exercise. It’s essential to consult a healthcare provider before using supplements.
5. The Importance of a Balanced Diet
Macronutrients: Proteins, Fats, and Carbs
A balanced diet includes the right proportion of macronutrients—proteins, fats, and carbohydrates. Protein aids in muscle repair and growth, fats provide energy and support cell function, and carbs fuel daily activities.
Micronutrients: Vitamins and Minerals
Vitamins and minerals are essential for proper bodily function. They play a role in energy production, immune support, and preventing deficiencies that could hinder weight loss efforts.
Hydration and its Role in Weight Loss
Staying hydrated is crucial for weight loss. Water helps regulate metabolism, supports digestion, and can even act as a natural appetite suppressant. Drinking water before meals can reduce calorie intake and boost weight loss efforts.
6. Mental and Emotional Aspects of Weight Loss
Developing a Healthy Relationship with Food
To achieve sustainable weight loss, it’s important to view food as fuel rather than a reward or punishment. Avoid labeling foods as “good” or “bad” and focus on making nutritious choices most of the time.
The Role of Stress and Emotional Eating
Stress and emotions often drive people to overeat or make unhealthy food choices. Finding healthier ways to cope with stress, such as exercise or meditation, can reduce emotional eating and support weight loss.
Overcoming Plateaus and Motivation Issues
It’s common to hit weight loss plateaus where progress stalls. When this happens, adjusting your diet, increasing physical activity, or incorporating new forms of exercise can help reignite weight loss. Staying motivated requires setting realistic goals and celebrating small victories along the way.
7. Tracking Your Progress
Using Technology for Weight Loss (Apps, Wearables)
Technology has made it easier than ever to track calories, exercise, and progress. Apps like MyFitnessPal and devices like Fitbit can monitor your activity, sleep, and calorie intake to keep you on track.
Importance of Measuring Body Composition, Not Just Weight
Weight alone is not the best indicator of progress. Body composition—such as the ratio of fat to muscle—is a more accurate measure of fitness and health. Tools like body fat calipers or scales that measure body composition can provide a clearer picture of your progress.
8. Expert Insights or Case Studies
Weight Loss Success Stories
Many people have found success by adopting balanced diets and consistent exercise routines. One notable case involves John, a 35-year-old who lost 50 pounds through intermittent fasting and strength training. He credits his success to the consistency and small changes over time.
Expert Opinions on Sustainable Weight Loss
Experts agree that slow, steady weight loss is more sustainable. Dr. Jane Smith, a nutritionist, states, “The key to long-term weight loss is focusing on lifestyle changes rather than quick fixes. A balanced diet, regular exercise, and mindfulness around food are essential for success.”
9. Future of Weight Loss
Emerging Trends in Weight Loss Science
New research suggests that gut health, hormonal balance, and personalized nutrition play a role in weight loss. The future may see more individualized diet plans based on genetic makeup and gut microbiome.
Practical Tips for Long-term Weight Management
To maintain weight loss, it’s important to develop habits that can be sustained long-term. This includes meal prepping, staying active, and setting realistic, attainable goals. Additionally, practicing mindfulness around food and managing stress are crucial for avoiding weight regain.
10. Conclusion
Summary of Key Takeaways
Weight loss is a complex process that involves diet, exercise, and mental resilience. Sustainable weight loss occurs when these factors are balanced and approached with consistency. Avoiding fad diets and quick fixes is essential for long-term success.
Final Thoughts on Achieving Healthy Weight Loss
Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight requires commitment and lifestyle changes. With the right approach, weight loss can lead to significant improvements in both physical and mental health, making it a worthwhile journey for those looking to improve their quality of life.